
Table of Contents
Cellular Access Point Names (APNs) play a critical role in connecting your cellular devices to the internet. Whether you’re using a smartphone, a hotspot, or a cellular router, the APN acts as the gateway between your device and the carrier’s network. Understanding how APNs work, why they’re important, and how to configure them manually can help ensure reliable connectivity, especially in situations where automatic settings fail.
History and Evolution of Cellular Access Point Names
Origins of APNs
Cellular access point names originated during the early days of mobile networks as a means to standardize connections between devices and carrier networks. As mobile technology evolved from basic voice communication to include data services, APNs became essential for routing data packets effectively. In the 2G and 3G eras, when mobile internet was first introduced, APNs allowed carriers to differentiate between types of data services, such as browsing the web, sending multimedia messages (MMS), and accessing private corporate networks.
Carriers assigned specific APNs to ensure that devices connected to the appropriate service gateways, thereby enabling reliable data transfers. These early APNs laid the foundation for today’s more complex and diverse configurations.
Modern Usage
In modern networks, cellular access point names have evolved to support a wide range of advanced features and use cases:
- 5G Connectivity: With the rollout of 5G networks, APNs now manage ultra-high-speed data connections and ensure low-latency communication for applications like augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and real-time gaming.
- Internet of Things (IoT): IoT devices rely on APNs to establish secure and reliable connections for transmitting data. For instance, smart meters and connected cars often use custom APNs tailored to their specific requirements.
- Private Networks: Enterprises use private APNs to create secure and isolated connections for their internal systems. These configurations allow businesses to maintain control over their data and reduce exposure to public network risks.
- Enhanced Authentication: Modern APNs often incorporate advanced authentication protocols to ensure that only authorized devices can access the network, thereby improving security.
This evolution underscores the adaptability of APNs in meeting the demands of an increasingly connected world. By enabling seamless communication across diverse devices and applications, APNs remain a cornerstone of cellular technology.
What Is an APN and How Does It Work?
An APN is a configuration setting on your device that identifies the network path for your cellular connection. It contains important information that enables your device to communicate with your carrier’s network, such as:
- The type of connection (e.g., internet or multimedia messaging service (MMS))
- Authentication details (if required)
- The carrier’s private IP settings
When a device attempts to connect to a cellular network, it retrieves the default APN assigned by the carrier. However, in some cases, a custom APN or manual configuration may be necessary.
Why Are Cellular Access Point Names Important?
APNs ensure that your device establishes a secure and correct connection to the carrier’s network. If an incorrect APN is applied, your device may fail to connect or experience limited functionality, such as the inability to access total available bandwidth. This is particularly important for:
- Custom Data Plans: Some carriers assign specific APNs for business or personal plans.
- IoT Devices: Devices in the Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem often require unique APNs for data communication.
- Cellular Routers: These devices sometimes fail to retrieve APNs automatically, requiring manual input to ensure connectivity.
When Should You Manually Configure an APN?
Manual configuration may be necessary in scenarios such as:
- Custom APNs: If your carrier provides a unique APN for your data plan, you’ll need to configure it manually.
- Automatic Configuration Failures: Some devices, especially cellular routers, may not automatically retrieve the correct APN.
- Network Troubleshooting: If your device is unable to establish a connection, updating or reapplying the APN might resolve the issue.
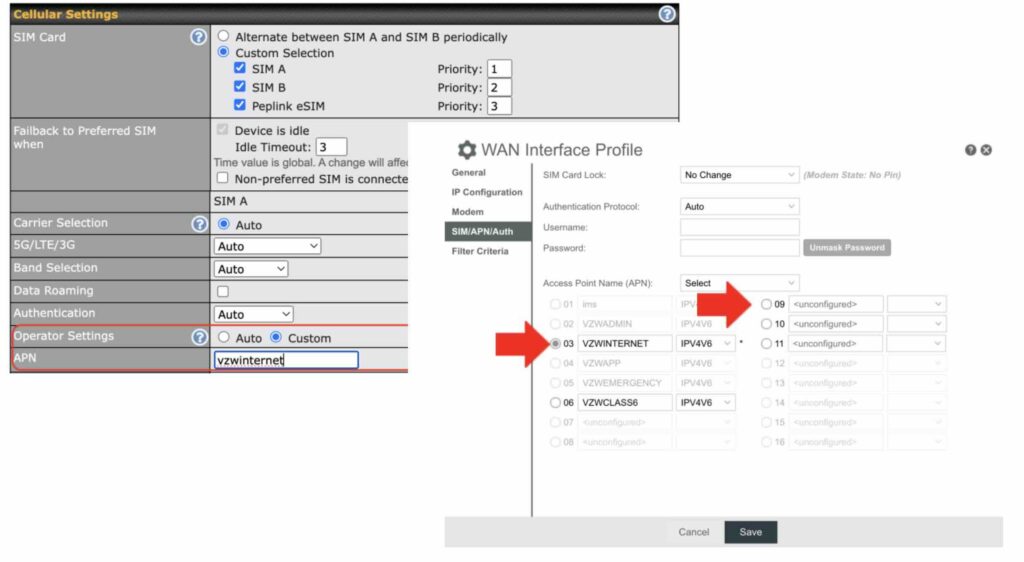
How to Apply an APN in a Cellular Router
To manually configure an APN in a cellular router, follow these steps:
- Log Into the Router’s Admin Page: Use your web browser to access the router’s admin page. Typically, this involves entering the router’s IP address (e.g., 192.168.1.1) into the browser’s address bar and logging in with the admin username and password.
- Navigate to Cellular Connection Settings: Locate the network section of the settings menu. Look for an option labeled “Cellular Settings” or similar, where APN configurations are found.
- Enter the APN Details:
- Refer to the APN provided by your carrier.
- If a username and password are required, include those details as well.
- Save and Apply Changes: Once the APN is entered, save the configuration. The router may disconnect temporarily before reconnecting with the updated settings.
- Test the Connection: Confirm that the router has successfully established a connection to the carrier’s network. If problems persist, double-check the APN details or contact your carrier for support.
For more information on how to apply the APN on common cellular routers, check out our YouTube Channel.
Known APNs by Carrier
Below is a sample table of APN configurations for some carriers. Be sure to verify the details with your provider, as APNs can vary by plan and region.
| Carrier | APN | Username | Password |
| AT&T | broadband | N/A | N/A |
| AT&T (static IP) | i2gold | N/A | N/A |
| T-Mobile | fast.t-mobile.com | N/A | N/A |
| T-Mobile (static IP) | b2b.static | N/A | N/A |
| Verizon 4G | vzwinternet | N/A | N/A |
| Verizon 5G | V5GA01INTERNET | N/A | N/A |
| Verizon 4G/ 5G (static IP) | mw01.vzwstatic ne01.vzwstatic so01.vzwstatic we01.vzwstatic nw01.vzwstatic | N/A | N/A |
Troubleshooting APN Issues
If your device fails to connect even after applying the correct APN, consider these troubleshooting tips:
- Double-Check the APN Details: Ensure there are no typos in the APN, username, or password.
- Reboot Your Device: Restart the router to refresh the connection.
- Verify Network Coverage: Confirm that your carrier’s network is available in your location.
- Contact Your Carrier: For persistent issues, reach out to your carrier’s support team for assistance.
Key Takeaways: Cellular Access Point Names
- APNs are vital for establishing a secure and functional cellular connection.
- While most devices retrieve APNs automatically, manual configuration may be necessary in certain situations.
- Understanding how to apply and troubleshoot APNs can ensure uninterrupted connectivity for your devices.
Whether you’re configuring a personal hotspot, a business router, or an IoT device, having the correct APN settings at your fingertips can save time and frustration. Keep a reference list of APNs handy and be ready to apply them as needed for seamless network access.

