Power sources play a crucial role in anything involved with electronics. Understanding the differences between Alternating Current (AC) and Direct Current (DC) can be essential. Additionally, the evolution of technology has introduced innovative solutions like Power over Ethernet (PoE), changing the way devices receive power and data. In this article we’ll explore details about different types of power sources and how they apply to our everyday lives.
AC vs. DC: The Basics
AC and DC refer to two distinct types of electric current. AC is characterized by the continuous change in the direction of the flow of electrons, making it the standard form of electricity distributed in homes and businesses. On the other hand, DC flows in a constant direction, making it ideal for electronic devices like smartphones, laptops, and electric cars.
Most electronic devices are designed to operate on DC power. Even devices with AC plugs, such as laptops and phone chargers, incorporate internal voltage converters that transform AC into DC current, ensuring compatibility with these devices. These converters, commonly known as power supplies or adapters, are available in various sizes, from small phone chargers to larger laptop power supplies.
Power Supply Connectors
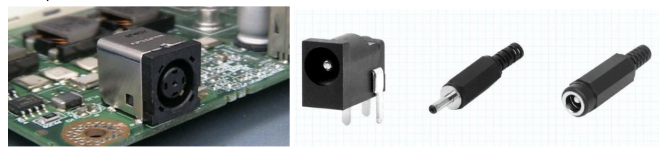
DC power connectors come in different shapes and sizes to cater to various devices. Examples include cylindrical connectors, barrel connectors, and USB connectors. AC connectors, typically used in larger devices, have their specific standards and shapes.
Examples of some DC connectors:
Examples of AC connectors:

Powering Network Devices
In networking setups, routers, switches, and Access Points (APs) require a stable power supply. For home and small business routers and switches, external AC adapters are commonly used, supplying the necessary power to these devices. Larger routers and switches utilize standard AC cables connected to internal power supplies, ensuring efficient power distribution.
Examples of some external power supplies:

Examples of some internal power supplies:

Power over Ethernet
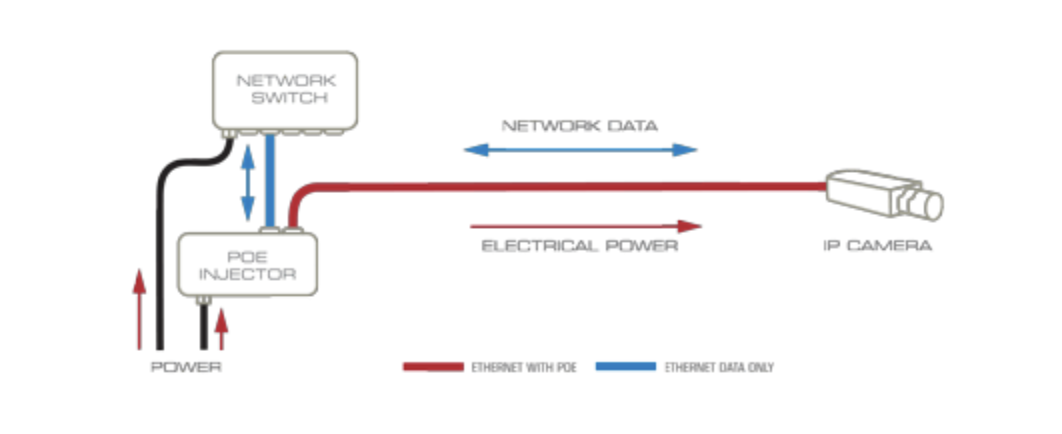
Power over Ethernet (PoE) has emerged as a game-changing technology in the world of networking. PoE enables both power and data transmission over a single Ethernet cable, simplifying installations and reducing clutter.
Types of PoE: Active vs. Passive
There are two main types of PoE: Active and Passive. Passive PoE delivers a constant voltage (such as 12 volts) over the Ethernet cable, with the connected device consuming the provided voltage. In contrast, Active PoE operates at standard voltages of 24 or 48 volts. The device at the end of the Ethernet cable communicates its voltage requirements to the PoE injector, which then supplies the precise voltage needed. Although they aren’t very common, PoE splitters can also be used in the cases that active PoE is the only option. For example, a 48V active splitter can provide 12V to a device that does not support PoE by negotiating the amount of power needed.
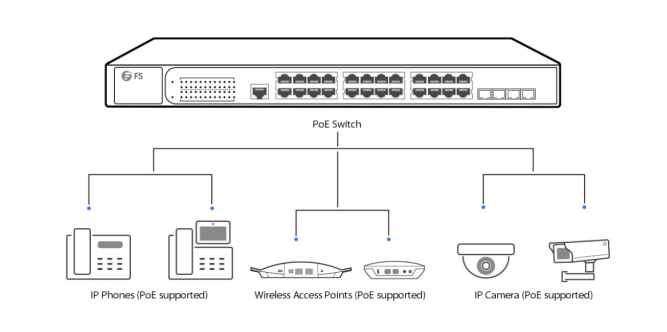
PoE Switches: A Convenient Solution
PoE switches further streamline the implementation of PoE technology. These switches have built-in PoE injectors, eliminating the need for separate PoE injectors. By integrating power and data delivery into a single device, PoE switches simplify network setups, especially in scenarios where multiple PoE devices need to be connected.