
Antennas play a critical role in the transmission and reception of cellular signals. They are designed to emit or receive electromagnetic waves, which carry information such as voice, data, and video, over the air. In the case of cellular networks, antennas are used to communicate between the mobile devices and the base stations. When you make a call or send a message on your smartphone, your device sends the signal to the nearest base station via an antenna, which then relays the signal to its destination.
But what about antenna frequencies? How do they impact cellular communication?
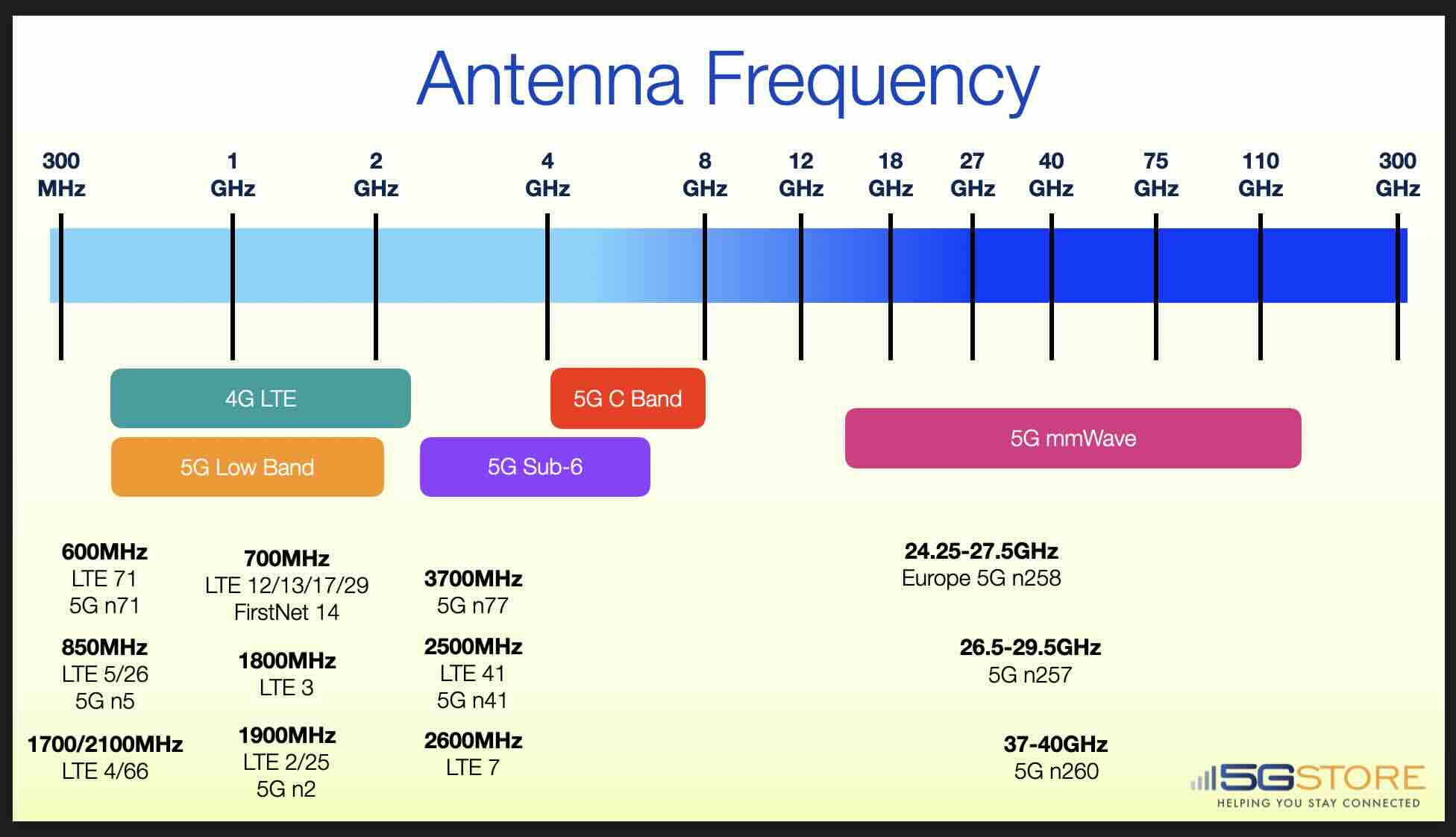
LTE (Long-Term Evolution) and 5G (5th Generation) cellular frequencies are used for wireless communication over cellular networks. LTE and 5G use various frequency bands depending on the region and the cellular operator. Generally speaking, LTE uses lower frequencies than 5G. Some are similar however, but are expanded to include additional frequency ranges (e.g. LTE Band 71 and 5G Band 71). It's important to note that frequency bands used by LTE and 5G vary between countries and network operators.
The use of different frequency bands can impact the speed, coverage, and penetration of wireless signals. Higher frequency bands can provide faster data speeds and lower latency, but they may have lower coverage and penetration compared to lower frequency bands. This is why it's important to choose the right antenna frequency for your specific use case. Whether you're building a cellular network, designing a wireless device, or simply trying to improve the signal quality on your smartphone or modem, understanding antenna frequencies is essential.
At 5Gstore.com, we specialize in providing high-quality antennas for cellular networks, WiFi, and GPS. Our antennas are designed to meet the specific needs of your project, whether you're looking for a low-cost solution for a small deployment or a high-performance antenna for a large-scale network.
5G Band n2 is a low-band frequency used for 5G New Radio (NR) networks, operating in the 1900 MHz spectrum. This band is an extension of the widely used PCS (Personal Communications Service) spectrum and has been historically utilized for 2G, 3G, and LTE networks. Band n2 is particularly valuable in ensuring strong network coverage and reliable connectivity in both urban and rural areas.
Extensive Coverage
As a low-band frequency, Band n2 provides broad coverage, making it ideal for connecting users across large areas, including rural and suburban regions. Its lower frequency allows signals to travel farther than mid-band and high-band frequencies.
Superior Building Penetration
One of the key advantages of Band n2 is its ability to penetrate obstacles such as walls, trees, and buildings more effectively than higher frequency bands. This ensures reliable indoor connectivity, reducing dead zones in homes, offices, and commercial spaces.
Foundation for Nationwide 5G Deployment
Many carriers use Band n2 as a fundamental part of their 5G rollout strategy. Because of its wide coverage, it serves as a crucial layer in nationwide 5G networks, complementing mid-band and high-band frequencies.
Seamless LTE to 5G Transition
Since Band n2 has been used for LTE, it allows carriers to repurpose existing infrastructure for 5G deployment. This makes it easier for mobile operators to provide 5G coverage without requiring significant new investments in network hardware.
Reliable Connectivity for IoT and Rural Networks
Band n2 is especially beneficial for Internet of Things (IoT) applications and rural broadband expansion. Its wide coverage and reliability make it suitable for applications like smart agriculture, remote monitoring, and critical infrastructure connectivity.
While Band n2 provides numerous benefits, there are some limitations to be aware of:
Limited Data Speeds: Being a low-band frequency, Band n2 does not support the ultra-fast speeds seen in mid-band (like Band n77) or high-band (mmWave) 5G deployments.
Network Congestion: Due to its broad coverage and use in multiple generations of wireless technology, Band n2 may experience network congestion in densely populated areas.
Carrier Deployment Variations: Not all carriers use Band n2 for 5G in every region, so availability may vary based on location and service provider.