
Antennas play a critical role in the transmission and reception of cellular signals. They are designed to emit or receive electromagnetic waves, which carry information such as voice, data, and video, over the air. In the case of cellular networks, antennas are used to communicate between the mobile devices and the base stations. When you make a call or send a message on your smartphone, your device sends the signal to the nearest base station via an antenna, which then relays the signal to its destination.
But what about antenna frequencies? How do they impact cellular communication?
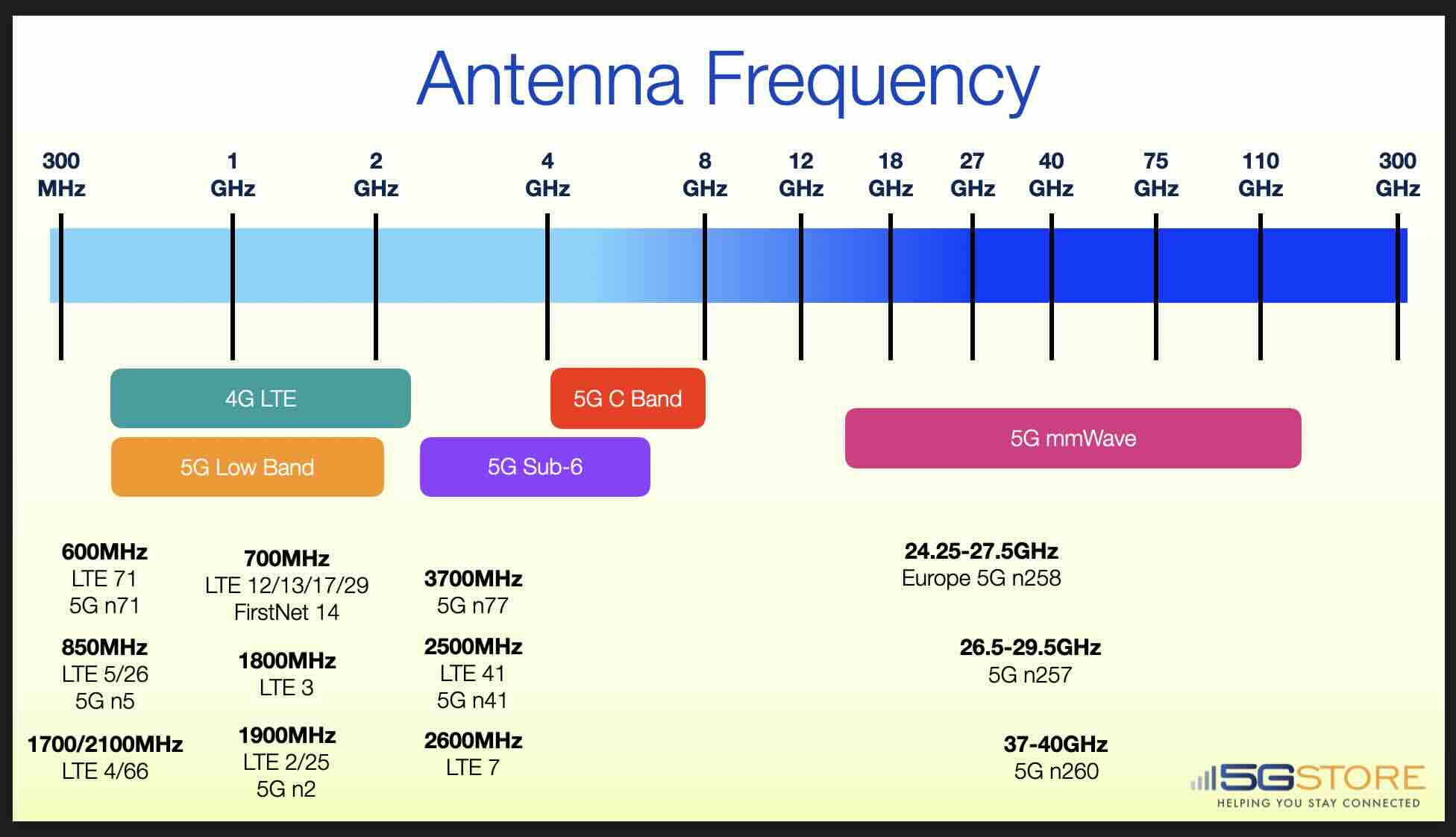
LTE (Long-Term Evolution) and 5G (5th Generation) cellular frequencies are used for wireless communication over cellular networks. LTE and 5G use various frequency bands depending on the region and the cellular operator. Generally speaking, LTE uses lower frequencies than 5G. Some are similar however, but are expanded to include additional frequency ranges (e.g. LTE Band 71 and 5G Band 71). It's important to note that frequency bands used by LTE and 5G vary between countries and network operators.
The use of different frequency bands can impact the speed, coverage, and penetration of wireless signals. Higher frequency bands can provide faster data speeds and lower latency, but they may have lower coverage and penetration compared to lower frequency bands. This is why it's important to choose the right antenna frequency for your specific use case. Whether you're building a cellular network, designing a wireless device, or simply trying to improve the signal quality on your smartphone or modem, understanding antenna frequencies is essential.
At 5Gstore.com, we specialize in providing high-quality antennas for cellular networks, WiFi, and GPS. Our antennas are designed to meet the specific needs of your project, whether you're looking for a low-cost solution for a small deployment or a high-performance antenna for a large-scale network.
5G Band n258 is a millimeter wave (mmWave) frequency band that operates in the 24.25 GHz to 27.5 GHz range. It is primarily allocated for 5G deployment in Europe and other regions worldwide. Band n258 enables ultra-fast speeds, low latency, and high-capacity networks, making it ideal for dense urban environments, enterprise applications, and industrial automation.
Gigabit-Level Data Speeds
Band n258 supports multi-gigabit per second (Gbps) data rates, enabling rapid downloads, seamless 4K/8K streaming, and high-speed enterprise connectivity.
Low Latency for Real-Time Applications
With ultra-low latency, Band n258 enhances real-time applications such as autonomous driving, smart manufacturing, and mission-critical communications.
High Network Capacity
This mmWave frequency supports large volumes of users in congested areas, making it ideal for stadiums, city centers, and transportation hubs.
Enhanced Private 5G Deployments
Enterprises can utilize Band n258 for secure and dedicated private 5G networks, boosting efficiency in industrial automation, logistics, and healthcare sectors.
Support for Next-Generation Technologies
Band n258 is optimized for innovations like AI-driven automation, augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and IoT advancements.
Despite its advantages, Band n258 has some challenges:
Limited Coverage Range: mmWave frequencies like Band n258 have shorter coverage areas compared to mid-band and low-band 5G.
Signal Penetration Issues: Obstacles such as buildings and trees can impact signal strength, requiring strategic deployment of small cells.
Deployment in High-Density Areas: Band n258 is best suited for urban centers, industrial zones, and enterprise solutions rather than broad rural coverage.