
Antennas play a critical role in the transmission and reception of cellular signals. They are designed to emit or receive electromagnetic waves, which carry information such as voice, data, and video, over the air. In the case of cellular networks, antennas are used to communicate between the mobile devices and the base stations. When you make a call or send a message on your smartphone, your device sends the signal to the nearest base station via an antenna, which then relays the signal to its destination.
But what about antenna frequencies? How do they impact cellular communication?
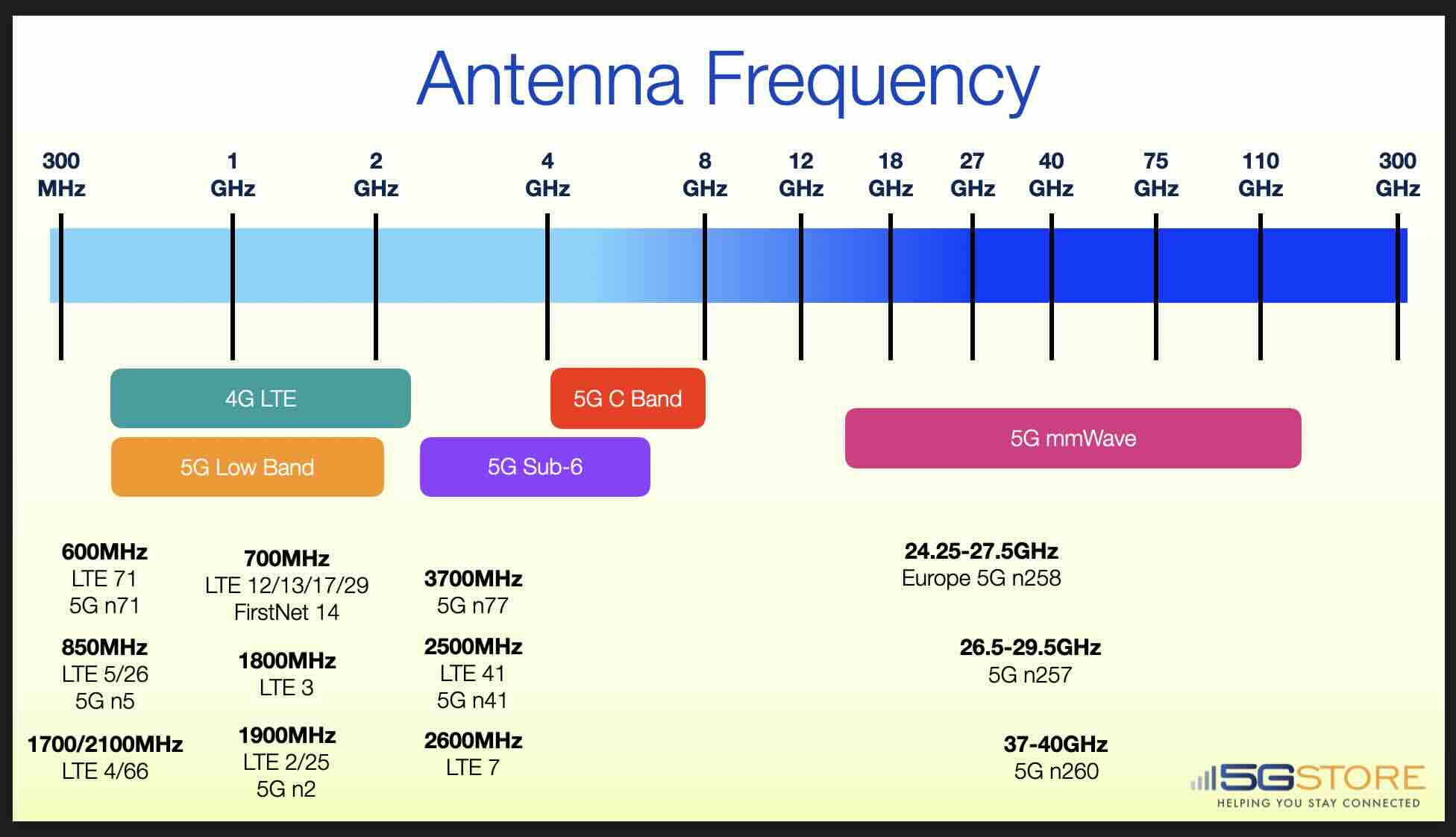
LTE (Long-Term Evolution) and 5G (5th Generation) cellular frequencies are used for wireless communication over cellular networks. LTE and 5G use various frequency bands depending on the region and the cellular operator. Generally speaking, LTE uses lower frequencies than 5G. Some are similar however, but are expanded to include additional frequency ranges (e.g. LTE Band 71 and 5G Band 71). It's important to note that frequency bands used by LTE and 5G vary between countries and network operators.
The use of different frequency bands can impact the speed, coverage, and penetration of wireless signals. Higher frequency bands can provide faster data speeds and lower latency, but they may have lower coverage and penetration compared to lower frequency bands. This is why it's important to choose the right antenna frequency for your specific use case. Whether you're building a cellular network, designing a wireless device, or simply trying to improve the signal quality on your smartphone or modem, understanding antenna frequencies is essential.
At 5Gstore.com, we specialize in providing high-quality antennas for cellular networks, WiFi, and GPS. Our antennas are designed to meet the specific needs of your project, whether you're looking for a low-cost solution for a small deployment or a high-performance antenna for a large-scale network.
5G Band n261 is a millimeter wave (mmWave) frequency band that operates between 27.5 GHz and 28.35 GHz. As part of the high-frequency spectrum, Band n261 is designed to deliver ultra-fast speeds and low-latency communication for next-generation applications. It is commonly used in high-density urban areas, enterprise deployments, and private 5G networks where high bandwidth and low congestion are essential.
Blazing-Fast Speeds
With multi-gigabit per second (Gbps) capabilities, Band n261 enables seamless ultra-HD video streaming, real-time cloud computing, and high-performance enterprise networking.
Ultra-Low Latency
The near-instantaneous response time of Band n261 makes it perfect for applications such as autonomous vehicles, remote-controlled robotics, and mission-critical industrial automation.
Increased Network Capacity
Operating in the mmWave spectrum, Band n261 supports a large number of simultaneous connections, reducing network congestion and improving overall performance in busy locations.
Private and Enterprise 5G Networks
Businesses and organizations are leveraging Band n261 for private 5G deployments, providing secure and high-speed connectivity for industrial operations, smart cities, and corporate campuses.
Advanced 5G Use Cases
From augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) experiences to next-gen healthcare applications, Band n261 supports a wide range of cutting-edge technologies that require high-speed, low-latency connectivity.
Despite its impressive capabilities, Band n261 comes with some challenges:
Shorter Coverage Range: Due to its high frequency, Band n261 has a more limited range compared to mid-band and low-band 5G frequencies, requiring a dense network of small cells for coverage.
Limited Penetration Through Obstacles: High-frequency signals struggle to penetrate buildings, trees, and other physical barriers, making outdoor deployment and line-of-sight crucial.
Urban and Enterprise-Focused Deployment: Band n261 is primarily available in densely populated areas and specialized private networks, meaning rural availability is limited.