
When it comes to networking, achieving high speeds and unwavering reliability for WAN connections is important to any business or power user. Bonding, a process that merges multiple internet connections into a unified, robust link, stands as a solution to this demand. Noteworthy among bonding technologies are Peplink SpeedFusion Bonding and Digi WAN Bonding, both renowned for their prowess in optimizing network performance.
Understanding Bonding Throughput
Throughput, in networking, refers to the rate of successful data transmission over a communication channel. In the realm of bonding, throughput hinges not only on individual connection speeds and reliability but also on the capabilities of the bonding router. Typically, the router’s throughput is going to be much higher than the bonded throughput. In any case though, the higher the router throughput, the higher the bonded throughput.
Peplink SpeedFusion Bonding
Peplink SpeedFusion harnesses patented technology to aggregate multiple WAN connections, morphing them into a single, high-performing bonded connection. This technology boasts three distinct features:
- SpeedFusion Hot Failover: In the event of a WAN disconnection, Hot Failover seamlessly transfers traffic to another connection while maintaining session persistence. This ensures uninterrupted operations even amidst connection hiccups.
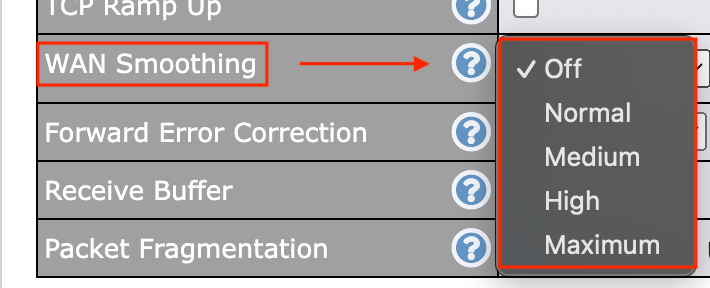
- SpeedFusion WAN Smoothing: Intelligent algorithms optimize connectivity by mitigating latency and minimizing the impact of packet loss. This works by using multiple WAN connections to send duplicate packets so that in the event that one WAN drops a packet, another picks it up. Be aware that this will create more data usage across your connections. WAN Smoothing is ideal for scenarios requiring reliability and responsiveness over sheer speed. For example, video meetings and voice calls have a much smoother connection.
- If you need to enable WAN Smoothing, find the ‘WAN Smoothing’ field within your SpeedFusion VPN profile configuration. This can be set to Normal (The total bandwidth consumption will be at most 2x of the original data traffic), Medium (3x the original traffic), High (4x the original traffic), and Maximum (The total bandwidth consumption depends on the number of connected active wan-to-wan connection).
- SpeedFusion Bandwidth Bonding: By combining data at the packet level, Bandwidth Bonding enables the aggregation of speeds from multiple connections, enhancing throughput significantly. This is particularly advantageous in bandwidth-constrained environments or when establishing connections between branch offices and headquarters. Throughput support is up to 4 Gbps with some models, but as low as 40 Mbps with others.
It should also be noted that there are different plans available to users that allow for a certain amount of bandwidth to be reached. This means even if your hardware is capable of supporting 1 Gbps over SpeedFusion, you may still be limited to below that amount. For example, if using Peplink’s SpeedFusion Connect (SF Connect) service plan that comes with your device’s warranty, you will only be able to achieve a max of 200 Mbps. However, if you opt for a different SF Connect plan, you may be able to achieve up to 400 Mbps. This is with plans that provide unlimited data usage for a specific period of time.
If neither of these options is sufficient to you, look at using Peplink’s FusionHub virtual appliance instead. This allows you to host your own SpeedFusion server on a cloud platform such as AWS or Microsoft Azure. You may also consider using another Peplink router at a site where you have access to a reliable, high-speed internet connection. As long as the bandwidth speed provided from the cloud or your personal Internet connection is faster than the speed your other Peplink is capable of supporting, you can set up a point to point connection between the routers. In either case, you are then able to obtain the full bandwidth the hardware is capable of supporting.
Digi WAN Bonding
Digi WAN Bonding leverages the power of Bondix Simple Aggregation of Networks (S.A.NE), combining multiple WAN links to boost throughput and maintain connection resilience. Key features include:
- Hot failover: Ensures continuous connectivity with zero packet loss or failover wait time.
- WAN aggregation: Combines multiple WAN links for enhanced speed and bandwidth, capable of achieving between 100 Mbps and 1 Gbps.
- Packet Duplication (WAN Smoothing): Minimizes latency and jitter by transmitting data through multiple channels simultaneously. Packets are replicated across multiple WAN links to safeguard the delivery of critical data. This allows packets to be received regardless of the WAN that sends them. If one WAN fails, the packets are received via another active channel.
- To enable this for your configuration, simply go into the device’s configuration settings and navigate to the ‘Network’ -> ‘SD-WAN’ -> ‘WAN Bonding’ section. Find ‘Mode’ and set this to ‘Packet Duplication.’ When ready, click ‘Apply’ at the top right to save the configuration.

- WAN prioritization: Automatically selects or allows manual configuration of the most optimal active WAN link, ensuring efficient traffic balancing.
- Simple integration: Facilitates easy deployment across diverse environments via Digi Remote Manager® (Digi RM).
Depending on the router model, Digi WAN Bonding offers varying throughput capacities. For instance, a Digi TX64 with three 200Mbps connections (Ethernet WAN + 2 cellular connections) can ensure up to 480Mbps bonded throughput.
Factors Influencing Throughput
Achieving optimal bonding throughput relies on a nuanced understanding of various influencing factors. Firstly, the number and types of WAN connections play a pivotal role. Diverse connections, such as DSL, cable, fiber, and cellular, each exhibit distinct characteristics in terms of speed, latency, and reliability. Consequently, selecting a combination of connections with complementary attributes can significantly impact overall throughput.
Moreover, cellular network congestion poses a formidable challenge to bonding throughput. During peak usage times or in densely populated areas, network congestion can lead to reduced speeds and increased latency, affecting the performance of bonded connections. Implementing congestion management techniques, such as Quality of Service (QoS) policies or traffic shaping, can mitigate these effects and maintain consistent throughput levels.
Router processing power constitutes another critical factor. Bonding routers must possess sufficient computational capabilities to handle the aggregation, segmentation, and reassembly of data packets across multiple connections efficiently. Inadequate processing power can bottleneck throughput and limit the effectiveness of bonding technology, especially in high-demand environments or when dealing with large volumes of data traffic.
Additionally, configuration settings play a crucial role in optimizing bonding throughput. Fine-tuning parameters such as load balancing algorithms and failover thresholds can significantly impact the efficiency and stability of bonded connections. By customizing these settings according to the specific requirements and characteristics of the network environment, users can maximize throughput while ensuring robustness and reliability.
Considerations for Users
When evaluating bonding solutions, users must carefully consider a range of factors to ensure the selection of a solution that aligns with their unique requirements and objectives. Firstly, desired throughput stands as a primary consideration. Different applications and use cases demand varying levels of bandwidth and speed. Whether the goal is to support high-definition video streaming, real-time communication, or large-scale data transfers, users must assess the bonding solution’s capacity to deliver the required throughput without compromising performance or reliability.
Budgetary considerations also play a significant role. Bonding solutions encompass a spectrum of costs, ranging from affordable consumer-grade options to enterprise-grade solutions with advanced features and scalability. Users must balance their budgetary constraints with the need for robustness, scalability, and long-term viability when selecting a bonding solution.
Scalability and future-proofing represent additional considerations. As businesses grow and network requirements evolve, bonding solutions must be capable of accommodating increasing bandwidth demands, additional connections, and emerging technologies. Choosing a solution that offers scalability through modular hardware, software upgrades, or flexible licensing models ensures long-term viability and minimizes the need for costly replacements or upgrades.
Compatibility with existing infrastructure is also paramount. Bonding solutions should seamlessly integrate with existing network components, protocols, and management systems to facilitate smooth deployment and operation. Compatibility considerations extend beyond technical interoperability to encompass factors such as ease of configuration, centralized management capabilities, and support for industry standards and protocols.
Lastly, support and maintenance considerations are crucial. Users should assess the availability of technical support, software updates, and maintenance services offered by bonding solution providers. Access to timely support, documentation, and firmware updates ensures ongoing reliability, security, and performance optimization of bonded connections.
By carefully evaluating these factors and conducting thorough research and testing, users can make informed decisions when selecting a bonding solution that meets their specific networking requirements, budget constraints, and long-term objectives.


