The way businesses connect to the internet has changed permanently. Fixed broadband works great until it doesn’t, and for remote sites, mobile deployments, or mission-critical operations where downtime is not an option, a 5G router is no longer a luxury. It’s infrastructure. Whether you’re running a construction trailer in a field, keeping a fleet of […]
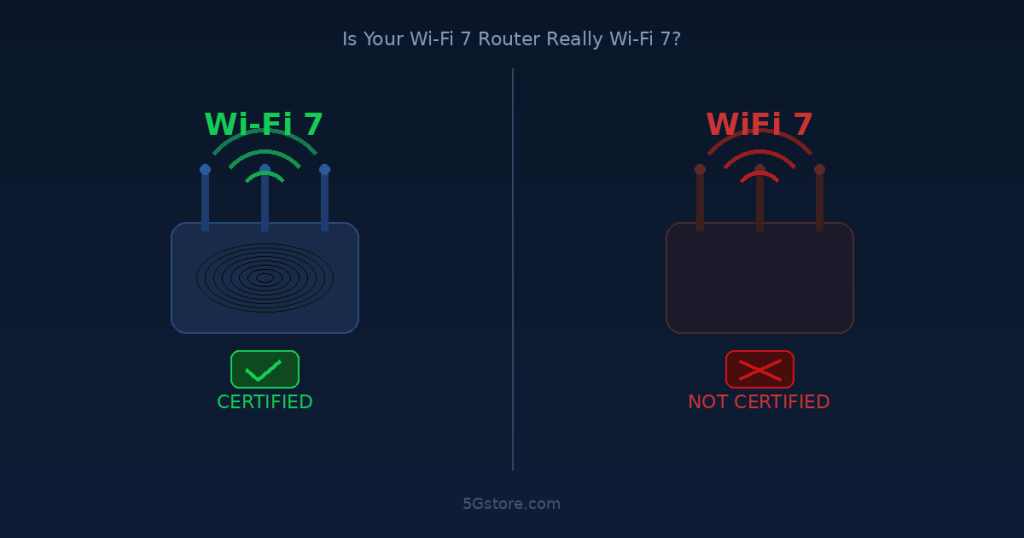
Is Your Wi-Fi 7 Router Actually Wi-Fi 7?
Is your WiFi 7 Router listed as WiFi 7 or Wi-Fi, missing the hypen or not? It matters Wi-Fi 7 has been marketed as the biggest leap in wireless technology in years. Faster speeds, lower latency, smarter band management — the promises are impressive. But there is a growing problem hiding in plain sight: a […]
Should You Use Google (8.8.8.8) or Cloudflare (1.1.1.1) DNS on Your Network
When people think about improving their internet experience, they usually focus on speed, signal strength, or their internet provider. One foundational setting that often gets overlooked is DNS (Domain Name System). DNS plays a critical role in how quickly and securely your devices reach websites and online services. Choosing the right DNS provider and configuring it […]
Ericsson Charts Its Own Path to AI-RAN With Custom Silicon — No Nvidia Required
The battle over what silicon should power the next generation of AI-enhanced 5G networks is heating up, and Ericsson just made its position crystal clear: you don’t need Nvidia to do AI-RAN. Two Nordic Giants, Two Very Different Strategies The 5G radio access network (RAN) equipment market is at a crossroads. As artificial intelligence becomes […]
KORE Wireless Acquired for $726M: What This IoT Going-Private Deal Means
KORE Group Holdings (NYSE: KORE), one of the largest independent IoT connectivity providers in the world, announced today that it has agreed to be acquired by private equity firms Searchlight Capital Partners and Abry Partners in an all-cash deal valued at approximately $726 million. Under the agreement, shareholders will receive $9.25 per share, and KORE […]
Taoglas TG.66 Series Review: The World’s Smallest 5G Antenna, Tested by 5Gstore
Summary: The Taoglas TG.66 is the world’s smallest 5G terminal mount antenna, covering the full 600 MHz to 6 GHz spectrum in a form factor barely larger than your thumb. We tested it at 5Gstore by replacing the larger stock antennas on several routers, and the TG.66 outperformed them. We also recommend swapping in the TG.66 […]
Starlink Cuts Prices and Offers Free Hardware to Distribution Partners: What It Means for Rural Internet Customers
Table of Contents SpaceX’s Starlink satellite internet service is making aggressive moves to expand its customer base, and the timing is hard to ignore. The company is now offering free hardware to distribution partners and cutting monthly service rates across multiple markets, a strategy CEO Elon Musk says is entirely about affordability — not competition. […]
AirLink OS 6.0 Now Available: What’s New for Your AirLink Router?
Semtech has released AirLink OS 6.0.0, a major new firmware version built exclusively for the new AirLink EX400 and RX400 5G RedCap routers. This isn’t just a point release — it’s the foundation for Semtech’s next generation of AirLink OS-powered industrial and commercial IoT routers, introducing a redesigned user interface, smarter cellular management, enhanced VPN configuration, and dozens […]
Peplink Is Going to Nasdaq: What the Plover Bay Spinoff Means
If you follow the networking world, and especially if you’re a Peplink user, you probably saw the big news today. Plover Bay Technologies (SEHK: 1523), the Hong Kong-listed parent company behind Peplink, has officially announced plans to spin off Peplink Holdings Ltd. as a separately listed company on the Nasdaq stock exchange. The transaction has […]
Taara Beam: This Shoebox-Sized Device Delivers 25Gbps Internet Using Invisible Beams of Light
What if you could get fiber-speed internet without laying a single cable? That’s the promise behind the Taara Beam, a compact wireless device that transmits data at up to 25Gbps using invisible near-infrared light — the same type of light used inside fiber optic cables, but sent through open air instead. Taara, which spun out of […]