
Table of Contents
5G has proven to be a reliable Internet service, offering faster internet speeds, lower latency, and a more reliable connection. However, as many users experience, 5G signal strength can vary greatly depending on the location, network conditions, and the device being used. If you’ve ever wondered what those signal bars on your phone really mean or how signal strength is determined, you’re not alone. Let’s take a closer look at 5G signal strength and how it impacts your device’s performance.
What Are Signal Bars?
Signal bars, those small icons on your phone’s screen, are one of the most common ways users gauge their device’s 4G or 5G signal strength. But what do they really represent? Signal bars are a visual indicator that provides a rough estimate of the strength of the connection between your device and the nearest cellular tower. The more bars you see, the stronger your connection is supposed to be, theoretically translating into faster speeds, more reliable calls, and less lag when using mobile data.
However, signal bars don’t always tell the full story. Different manufacturers may use different algorithms to calculate the number of bars, and some devices might exaggerate the strength of the signal. So, while the bars give a general idea, they can be somewhat misleading when it comes to understanding your actual connection quality.
How Is 4G and 5G Signal Strength Determined?
Signal strength is primarily measured by a few key factors in the case of 4G and 5G technologies.
- RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indicator): RSSI is a measure of the power level received by your phone’s antenna. It tells you how strong the signal is, but it doesn’t account for the quality of the signal or the noise level. Higher RSSI values typically correspond to better signal strength, but RSSI alone can’t always predict your connection speed or reliability.
- RSRP (Reference Signal Received Power): RSRP is specific to LTE (4G) and 5G networks. It measures the power of a specific reference signal sent from the base station (or cell tower). RSRP is more useful for determining signal strength because it reflects the actual quality of the connection between your device and the tower. In the case of 5G, a higher RSRP generally translates to better speed and reliability.
- RSRQ (Reference Signal Received Quality): RSRQ measures signal quality by evaluating the ratio of RSRP to total received power (RSSI). Typical Range: -3 dB (excellent) to -19.5 dB (poor). It indicates network congestion or interference. Even with good RSRP, poor RSRQ can lead to slow speeds. RSRQ tells you how clean the signal is—less interference means better quality.
- SINR (Signal-to-Interference-plus-Noise Ratio): SINR measures the ratio of usable signal to interference and noise. Typical Range: 20+ dB (excellent), 0 dB (poor), negative values (unusable). A high SINR means faster speeds and better performance. Even with strong RSRP, poor SINR can result in slow or unstable connections. SINR is like a signal-to-noise filter—the clearer the signal, the better the performance.
How Does 5G Signal Strength Differ from 4G?
5G is designed to deliver faster and more reliable connections, but achieving this goal depends largely on signal strength. The 5G network operates across a variety of frequency bands, each offering different ranges and speeds. These bands are often categorized as:
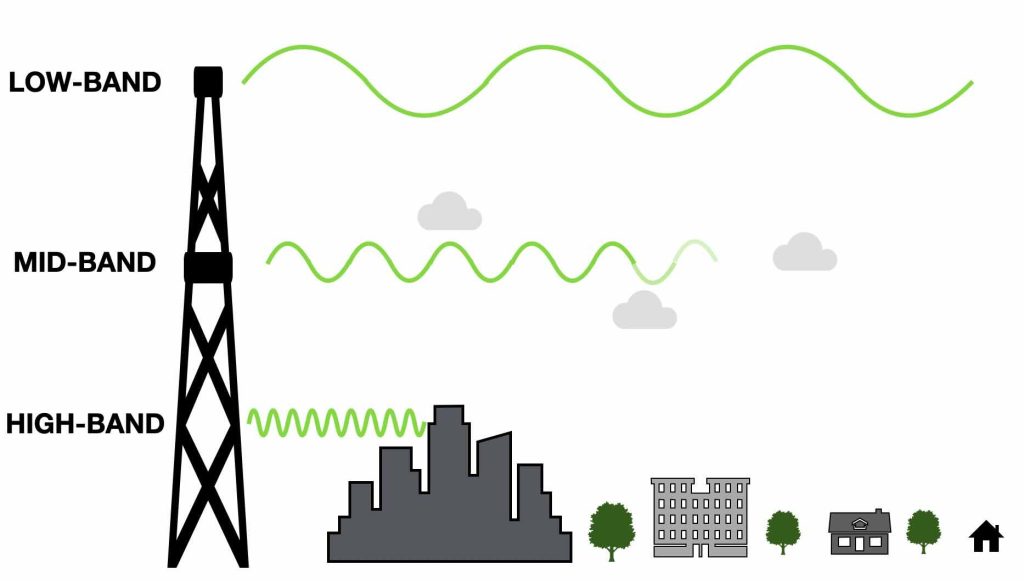
- Low-Band 5G: This offers wide coverage and better penetration through buildings, but it may not provide the ultra-fast speeds that 5G is known for. Its signal strength is similar to or slightly better than 4G in terms of coverage.
- Mid-Band 5G (Sub-6 GHz): This offers faster speeds and better overall performance, but its range is more limited compared to low-band 5G. This type of signal strength tends to degrade faster as you move away from the tower.
- High-Band 5G (mmWave): This provides incredibly fast speeds and low latency but has a much shorter range and can struggle to penetrate buildings or other obstacles. In ideal conditions, this offers the highest signal strength, but performance drops significantly as you move further away from the tower or in areas with many obstructions.
As 5G networks evolve, different regions may have varying levels of 5G coverage, meaning the signal strength you experience can differ greatly depending on your location.
What Affects 5G Signal Strength?
Several factors can affect how strong your 5G signal is. These include:
- Distance from the Tower: The closer you are to a cellular tower, the stronger your signal will be. As you move farther away, the signal weakens.
- Obstructions: Physical barriers such as buildings, trees, and even weather conditions (like rain or fog) can block or reflect the signal, reducing strength.
- Network Congestion: During peak usage times, when many people are trying to access the network, the available bandwidth may be limited, causing slower speeds and a drop in signal strength.
- Device Limitations: The phone or device you use also plays a crucial role in determining signal strength. Older devices or those that do not support certain 5G bands may not perform well in areas with 5G coverage.
- Interference: Electromagnetic interference from other electronic devices can affect signal quality. For example, Wi-Fi networks, microwaves, and other radio signals can interfere with 5G frequencies.
How Does Signal Strength Impact Your Device’s Performance?
Signal strength has a direct impact on your device’s ability to perform everyday tasks like browsing the web, streaming videos, and making calls. Here’s how it breaks down:
- Weak Signal: When the signal strength is low, you might experience slower data speeds, dropped calls, and poor video quality during streaming. If you’re using a 5G connection, you may also fall back to 4G or 3G if the 5G signal isn’t strong enough.
- Strong Signal: A strong signal provides the opposite effect—fast download and upload speeds, low latency, and clearer voice calls. This is particularly important for activities like online gaming, HD video calls, and heavy data consumption like streaming 4K videos.
Conclusion: Signal Bars Are Just the Beginning
While signal bars can give you a basic understanding of your device’s connection quality, they don’t offer a complete picture of your network performance. Understanding factors like RSSI, RSRP, and the type of 5G band being used can help you get a better grasp of why your signal strength might fluctuate and how it impacts your day-to-day use of mobile data. For additional information on finding and Understanding RSSI, RSRP, and RSRQ you can visit one of our other 5Gstore blogs.
As 5G networks continue to expand, improving coverage and optimizing signal strength will become key factors in delivering on the promises of faster, more reliable mobile experiences. So, while signal bars are handy, they’re just a starting point. If you’re looking for optimal performance, understanding the complexities of signal strength will give you a deeper insight into how to make the most of your 5G connection. Once you have a foundational understanding of what goes into a strong connection you can begin to explore how to improve connectivity.

