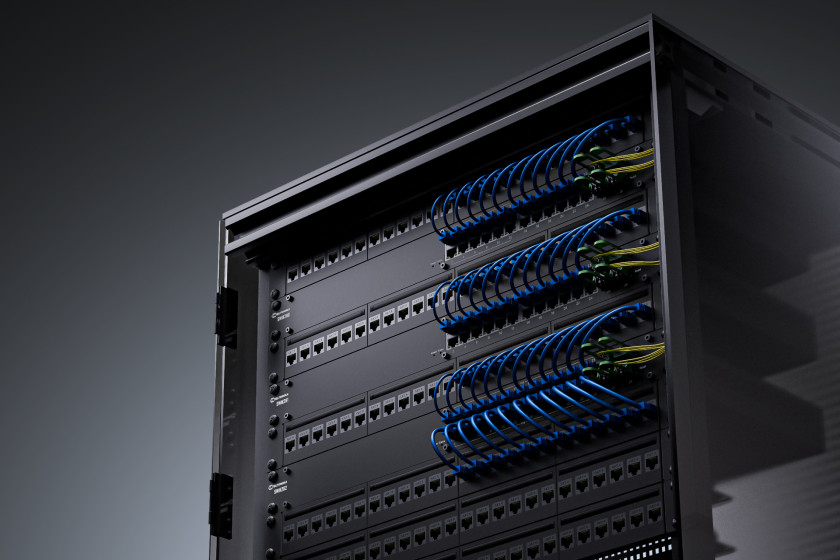
Introduction Teltonika Networks has long been known for providing rugged, reliable, and innovative networking hardware for industrial and enterprise environments. From their popular cellular routers and gateways to their growing line of industrial switches, Teltonika continues to build solutions that meet the demands of modern connectivity. With the launch of the SWM28-series managed switches—including the SWM280, SWM281, and SWM282—Teltonika […]
EV Charging with 5G: How Cellular Routers Keep Stations Connected
How to Use Cellular Routers for EV Charging: Keeping Your Chargers Online, Always Introduction As EV adoption soars, reliable connectivity for EV chargers is more critical than ever. Whether at workplaces, public parking, or fleet depots, maintaining a stable, secure link to the internet ensures seamless operation, diagnostics, payment processing, firmware updates, and analytics. At 5Gstore, […]
How to Use Your iPhone or Android to Test All 3 Major Carriers – The Ultimate Carrier Site Survey from Your iPhone or Android
When it comes to mobile connectivity, not all carriers perform equally in every location. Coverage maps only tell part of the story; real-world performance depends on signal strength, tower load, and even the terrain around you. That’s why professionals—whether they’re IT managers, RV travelers, or field engineers—often perform carrier site surveys before deciding on a network. In […]
Amphenol’s buying spree is reshaping the broadband vendor landscape, here’s what it means for ISPs and integrators
Over the past few weeks, interconnect giant Amphenol has moved from “quiet component powerhouse” to headline-grabbing consolidator in broadband and adjacent markets. The company is rapidly becoming a much bigger player in the overall fiber cabling and connector business, with competitors now including Corning, TE Connectivity, Belden, Molex, and Prysmian. Below is a quick summary […]
Peplink Firmware 8.5.3 RC1 – New Features, Fixes, and Download Guide
Peplink has released Firmware 8.5.3 RC1 (Release Candidate 1), bringing the platform closer to its official release. As with any RC build, this version is intended for testing and validation, and while it introduces many new features and bug fixes, we recommend caution before deploying it on production routers. Peplink 8.5.3 Supported Devices Firmware 8.5.3 […]
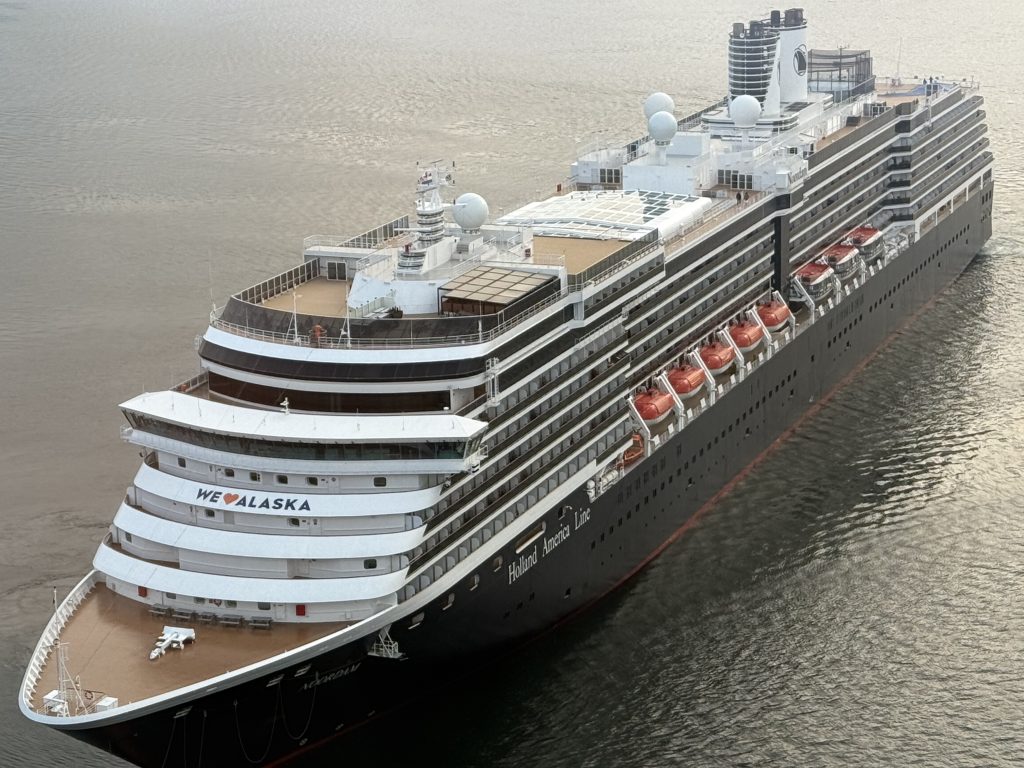
Alaska Cruise Connectivity 2025: Verizon vs AT&T vs T-Mobile vs Starlink Wi-Fi
Introduction Alaska is one of the most breathtaking cruise destinations in the world—but it’s also one of the most challenging when it comes to cellular connectivity. Rugged mountains, fjords, remote towns, and sparse infrastructure mean that coverage varies dramatically by location and carrier. But if you need to stay connected which carrier offers the best Alaska […]
Urgent Notice: InControl 2 Outage – Cloud Management Currently Experiencing Issues
UPDATE – 12:10pm CDT Per Peplink support: Our engineering team has implemented a fix, and the platform is now stable. You should begin to see your devices gradually coming back online. We are continuing to monitor the situation closely to ensure full recovery. We sincerely apologize for any inconvenience this may have caused. For the […]
What Sets Teltonika Apart: 5 Examples of Reliable Industrial Routers
Part 2 of Our Series: Discovering Teltonika Networks – Take a closer look at some of the most popular devices from Teltonika – RUT241, RUT956, RUTX11, and RUTM50 – in action! Welcome to Part 2 of our ongoing series exploring Teltonika Networks, where we’re diving into the tech, tools, and real-world use cases. Read along […]
Peplink Firmware 8.5.3 Beta 2: Major Improvements, Critical Bug Fixes, and New Features
Peplink Firmware 8.5.3 Beta 2 — Full Release Summary and Bug Fix Highlights Peplink has officially released Firmware 8.5.3 Beta 2 (August 13, 2025), bringing a wealth of feature enhancements, stability improvements, and critical bug fixes across its extensive lineup of Balance, MAX, UBR, B One, MediaFast, SDX, EPX, PDX, and FusionHub devices. In this post, we’ll cover: Supported […]
MG90 Firmware Update Required Before Certificate Expiration
Semtech (formerly Sierra Wireless) has issued an urgent reminder for customers using AirLink® MG90 devices. If your MG90 firmware is version 4.4.2.0 or older, you must take immediate action to prevent a loss of remote management capabilities through AM/AMM platforms. Why This Update Matters A management certificate in MG90 firmware 4.4.2.0 and older is set […]